X 2 4 X 1
sicesbrasil
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
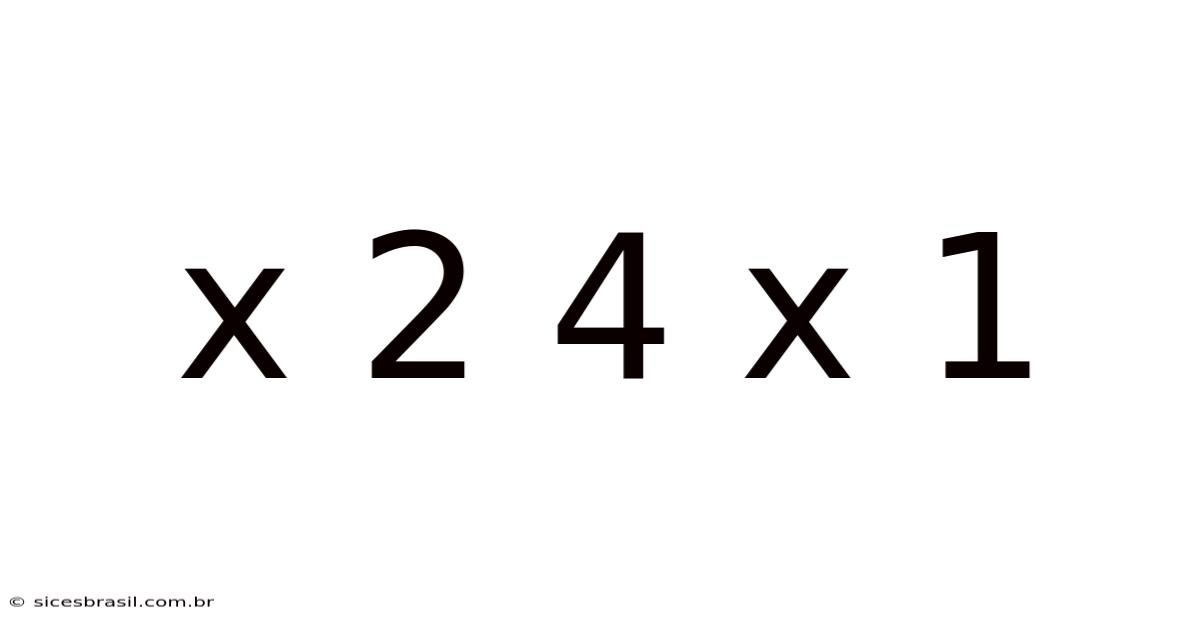
Table of Contents
Decoding the Mystery: A Deep Dive into the Expression "x² + 4x + 1"
This article explores the mathematical expression x² + 4x + 1, examining its properties, how to solve it, and its applications in various fields. Understanding quadratic equations like this is fundamental to algebra and forms the basis for more advanced mathematical concepts. We will cover everything from basic factorization to the quadratic formula and delve into its graphical representation. This comprehensive guide is designed for students, educators, and anyone curious about the beauty and power of mathematics.
Understanding Quadratic Equations
Before we dive into the specifics of x² + 4x + 1, let's establish a foundational understanding of quadratic equations. A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation of the second degree, meaning the highest power of the variable (in this case, x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants, and a is not equal to zero (otherwise, it wouldn't be a quadratic equation).
In our specific case, x² + 4x + 1, we have a = 1, b = 4, and c = 1. This means we're dealing with a monic quadratic equation (where the coefficient of x² is 1), making some calculations simpler.
Methods for Solving x² + 4x + 1 = 0
Solving a quadratic equation means finding the values of x that make the equation true. There are several methods we can use:
1. Factoring
Factoring involves rewriting the quadratic expression as a product of two linear expressions. Unfortunately, x² + 4x + 1 doesn't factor neatly using integers. While some quadratic equations can be easily factored, this one requires a more advanced approach. We'll look at those next.
2. Completing the Square
Completing the square is a powerful technique that transforms the quadratic equation into a perfect square trinomial, making it easy to solve. Here's how it works for x² + 4x + 1 = 0:
- Move the constant term to the right side: x² + 4x = -1
- Take half of the coefficient of x (which is 4), square it (4/2 = 2, 2² = 4), and add it to both sides: x² + 4x + 4 = -1 + 4
- Rewrite the left side as a perfect square: (x + 2)² = 3
- Take the square root of both sides: x + 2 = ±√3
- Solve for x: x = -2 ± √3
Therefore, the solutions are x = -2 + √3 and x = -2 - √3. These are the exact solutions.
3. The Quadratic Formula
The quadratic formula is a universal method for solving any quadratic equation. It's derived from completing the square and provides a direct way to find the solutions. The formula is:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
Substituting our values (a = 1, b = 4, c = 1), we get:
x = [-4 ± √(4² - 4 * 1 * 1)] / (2 * 1) x = [-4 ± √(16 - 4)] / 2 x = [-4 ± √12] / 2 x = [-4 ± 2√3] / 2 x = -2 ± √3
As expected, we arrive at the same solutions as with completing the square.
The Discriminant: Unveiling the Nature of Solutions
The expression inside the square root in the quadratic formula (b² - 4ac) is called the discriminant. It provides valuable information about the nature of the solutions:
- If b² - 4ac > 0: The equation has two distinct real solutions. This is the case with x² + 4x + 1, as the discriminant (12) is positive.
- If b² - 4ac = 0: The equation has one real solution (a repeated root).
- If b² - 4ac < 0: The equation has two complex conjugate solutions (solutions involving imaginary numbers).
Graphical Representation: Visualizing the Quadratic
The equation x² + 4x + 1 = 0 represents a parabola. Parabolas are symmetrical U-shaped curves. The solutions to the equation are the x-intercepts (where the parabola crosses the x-axis). Since we found two real solutions, the parabola intersects the x-axis at two distinct points.
The vertex of the parabola, the lowest point, can be found using the formula x = -b/2a. In our case, x = -4/(2*1) = -2. Substituting this value back into the equation gives the y-coordinate of the vertex: y = (-2)² + 4(-2) + 1 = -3. Therefore, the vertex is at (-2, -3).
Understanding the graphical representation helps visualize the solutions and provides a geometric interpretation of the quadratic equation.
Applications of Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they have numerous real-world applications across various fields:
- Physics: Projectile motion, where the height of a projectile over time follows a parabolic trajectory, is described by a quadratic equation.
- Engineering: Designing bridges, arches, and other structures often involves quadratic equations to determine optimal shapes and stability.
- Economics: Quadratic functions are used in modeling cost, revenue, and profit functions to optimize business decisions.
- Computer Graphics: Creating curved lines and shapes in computer graphics utilizes quadratic equations and related concepts like Bézier curves.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I solve x² + 4x + 1 = 0 using a calculator?
A: Yes, most scientific calculators have a quadratic equation solver function. You simply input the values of a, b, and c, and the calculator will provide the solutions.
Q: What if the coefficient of x² is not 1?
A: The methods described (completing the square and the quadratic formula) work for any quadratic equation, regardless of the value of a. However, factoring might become more challenging.
Q: Are there other ways to solve quadratic equations?
A: Yes, numerical methods like the Newton-Raphson method can be used to approximate solutions, especially for equations that are difficult to solve analytically.
Q: What does it mean when the solutions are complex numbers?
A: Complex numbers involve the imaginary unit i, where i² = -1. In the context of quadratic equations, complex solutions indicate that the parabola does not intersect the x-axis; it lies entirely above or below the x-axis.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple expression x² + 4x + 1 encapsulates a wealth of mathematical concepts and applications. From understanding the fundamentals of quadratic equations to applying the quadratic formula and visualizing the parabola, we've explored this expression thoroughly. Mastering the techniques discussed here is crucial for anyone pursuing further studies in mathematics, science, or engineering. Remember, the key is to understand the underlying principles and choose the most appropriate method to solve the equation at hand. The beauty of mathematics lies in its elegance and its ability to unravel the complexities of the world around us, one equation at a time.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 2 4 X 1 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.