What Is 2 X 2
sicesbrasil
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
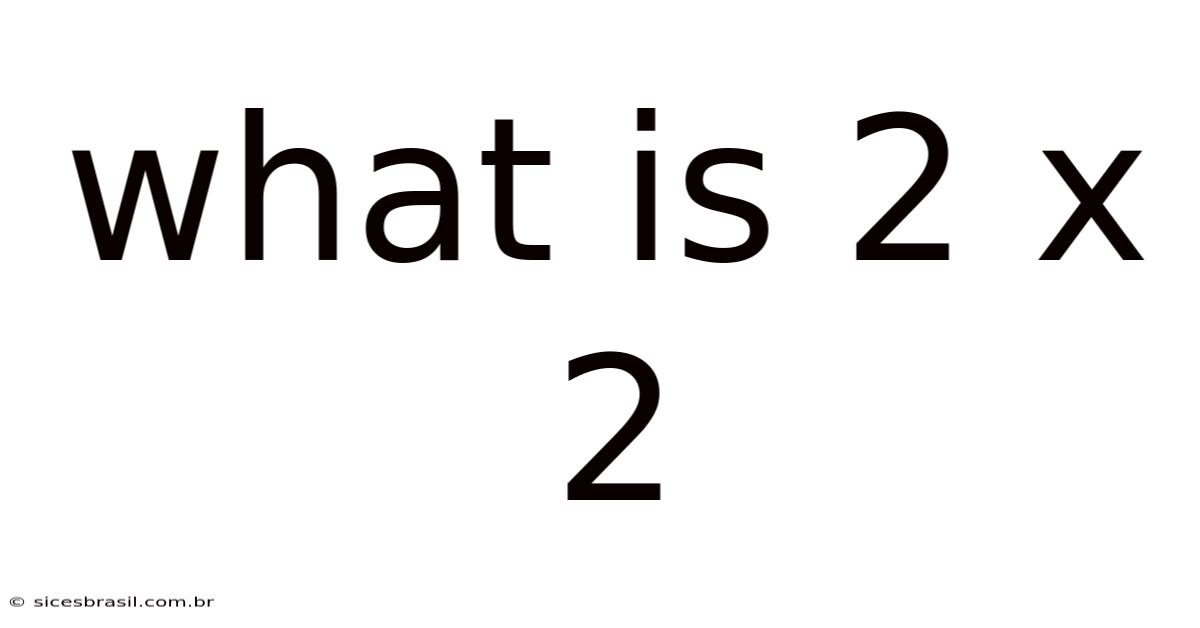
Table of Contents
What is 2 x 2? A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
What is 2 x 2? At first glance, this seems like a trivially simple question, a problem suitable for a kindergartner. The answer, 4, is readily apparent. But beyond the immediate answer lies a wealth of mathematical concepts, historical context, and practical applications that illuminate the fundamental nature of multiplication and its importance in various fields. This article will explore the seemingly simple question "What is 2 x 2?" in much greater depth than you might expect, uncovering its significance in mathematics, science, and everyday life.
Understanding Multiplication: Beyond Simple Addition
Before delving into the intricacies of 2 x 2, let's establish a firm understanding of multiplication itself. Multiplication is essentially a shortcut for repeated addition. When we say 2 x 2, we are essentially asking: what is the sum of two 2s? This can be written as 2 + 2 = 4. This simple example demonstrates the fundamental relationship between addition and multiplication.
However, multiplication's power extends far beyond simple repeated addition. It forms the basis of numerous advanced mathematical concepts and is indispensable in fields ranging from engineering to finance. Its efficiency makes it crucial for tackling complex calculations swiftly and accurately. Consider, for example, calculating the area of a square with sides of length 2 units. Using multiplication, we simply calculate 2 x 2 = 4 square units, a far more efficient method than adding the area of four individual 1x1 squares.
The Number 4: A Closer Look at the Result
The result of 2 x 2, the number 4, holds its own significance in mathematics. It is:
- An even number: Meaning it is divisible by 2 without leaving a remainder.
- A composite number: Meaning it has factors other than 1 and itself (2 and 2 being the factors).
- A perfect square: Meaning it is the product of a number multiplied by itself (2 x 2).
- The smallest composite number: The first composite number encountered after 1, 2, and 3, which are prime.
This seemingly simple number is fundamental to several mathematical concepts. For example, it plays a crucial role in base-4 number systems, various geometric calculations, and even advanced mathematical concepts.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Multiplication
The concept of multiplication, while seemingly intuitive today, evolved gradually throughout history. Early civilizations, lacking a formal system of multiplication, likely used methods like repeated addition to perform calculations. The development of different numeral systems, from Egyptian hieroglyphs to Roman numerals and eventually the Hindu-Arabic system we use today, significantly impacted the ease and efficiency of multiplication. The invention of the abacus and later, the development of algorithms for multiplication, further revolutionized how we approach this fundamental operation. The progression from concrete representation (using pebbles or fingers) to abstract symbols represents a crucial shift in mathematical thought and laid the foundation for more complex mathematical developments.
Applications of Multiplication: From Everyday Life to Advanced Science
The seemingly simple equation, 2 x 2 = 4, has widespread practical applications across numerous fields:
- Everyday Finances: Calculating the cost of two items at $2 each. Calculating the total earnings from two hours of work at $2 per hour.
- Cooking and Baking: Doubling a recipe that calls for 2 cups of flour. Calculating the total number of cookies from two batches of 2 cookies each.
- Construction and Engineering: Calculating the area of a floor tile (2x2 feet). Determining the total length of two beams, each 2 meters long.
- Computer Science: Basic arithmetic operations in programming languages. Binary calculations (base-2) heavily rely on the principles of multiplication.
- Physics and Engineering: Numerous physics equations involve multiplication. Calculating forces, velocities, and accelerations often require multiplication. For example, calculating the kinetic energy of an object requires squaring its velocity, which intrinsically utilizes multiplication.
- Chemistry: Stoichiometry, the study of quantitative relationships in chemical reactions, heavily relies on multiplication to determine the amounts of reactants and products involved in a reaction.
These are just a few examples. The pervasiveness of multiplication in everyday life and specialized fields underscores its fundamental importance in both practical and theoretical contexts.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring More Complex Multiplications
While 2 x 2 is a simple example, the principles of multiplication extend to far more complex scenarios:
- Multiplying larger numbers: The same principles apply when multiplying larger numbers. Understanding place value and the distributive property becomes crucial for efficient multiplication of larger numbers.
- Multiplying fractions: Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators together and the denominators together.
- Multiplying decimals: Multiplying decimals requires careful attention to place value and the movement of the decimal point.
- Multiplying negative numbers: The rules for multiplying negative numbers are crucial to understand: a negative number multiplied by a positive number results in a negative number, and a negative number multiplied by a negative number results in a positive number.
Mastering these advanced aspects of multiplication opens doors to more complex mathematical concepts and problem-solving abilities.
The Role of Multiplication in Algebra and Calculus
Multiplication forms the cornerstone of algebra and calculus. In algebra, it's essential for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and working with variables. In calculus, derivatives and integrals often involve multiplication and its inverse, division. Concepts like the product rule and chain rule in calculus demonstrate the intricacies of multiplication in advanced mathematical contexts. The ability to manipulate algebraic expressions efficiently hinges on a thorough understanding of multiplication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: What is the commutative property of multiplication?
A: The commutative property states that the order of the numbers being multiplied does not affect the result. For example, 2 x 2 is the same as 2 x 2. This property is fundamental and simplifies many calculations.
-
Q: What is the associative property of multiplication?
A: The associative property states that the grouping of numbers being multiplied does not affect the result. For example, (2 x 2) x 2 is the same as 2 x (2 x 2). This is particularly useful when dealing with multiple factors.
-
Q: How does multiplication relate to division?
A: Multiplication and division are inverse operations. If you multiply a number by another number and then divide the result by the second number, you will get back the original number. They are two sides of the same coin.
-
Q: What are some real-world examples of multiplication beyond the simple 2 x 2?
A: Calculating the area of a rectangular room (length x width), determining the total cost of multiple items at the same price, figuring out the total distance traveled at a constant speed over a period of time. Applications are virtually limitless across various fields.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of 2 x 2
The question, "What is 2 x 2?" may appear simplistic. However, as we've explored, this seemingly elementary calculation opens a window into the vast world of mathematics, revealing its foundational role in numerous fields. From everyday financial transactions to advanced scientific calculations, multiplication, and the simple example of 2 x 2, represents a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. A deep appreciation of this fundamental operation empowers us to navigate a wide range of challenges and explore the complexities of the world around us with greater clarity and precision. The seemingly simple answer, 4, is a gateway to a universe of mathematical possibilities.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 2 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.