Factorise X 2 4x 12
sicesbrasil
Sep 23, 2025 · 5 min read
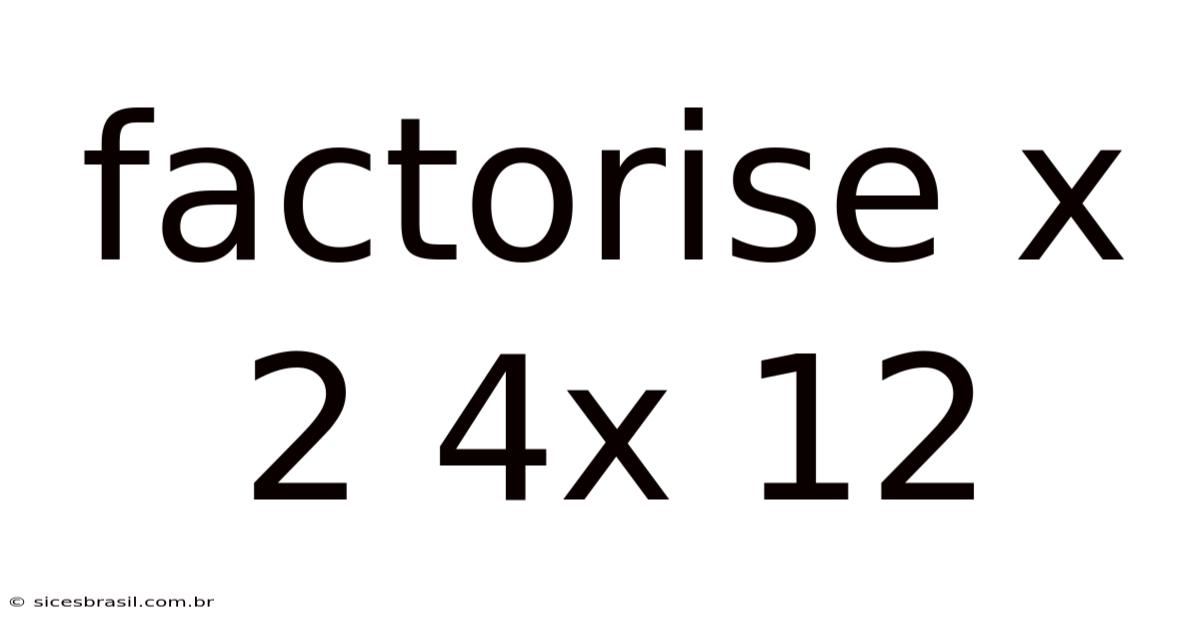
Table of Contents
Factoring Quadratic Expressions: A Deep Dive into x² + 4x + 12
Factoring quadratic expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra. Understanding how to factor allows you to solve quadratic equations, simplify complex expressions, and gain a deeper understanding of mathematical relationships. This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to factor the quadratic expression x² + 4x + 12, exploring various methods and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll also address common misconceptions and provide strategies for tackling similar problems.
Understanding Quadratic Expressions
A quadratic expression is a polynomial of degree two, meaning the highest power of the variable (usually x) is 2. The general form of a quadratic expression is ax² + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. Our target expression, x² + 4x + 12, fits this form with a = 1, b = 4, and c = 12. Factoring involves rewriting the expression as a product of simpler expressions.
Attempting to Factor x² + 4x + 12 using Common Methods
The most common methods for factoring quadratic expressions are:
-
Finding common factors: This involves looking for a common factor among all terms. In x² + 4x + 12, there are no common factors among x², 4x, and 12.
-
Difference of squares: This applies to expressions of the form a² - b², which factors to (a + b)(a - b). Our expression is not a difference of squares.
-
Perfect square trinomial: This applies to expressions of the form a² + 2ab + b², which factors to (a + b)². Similarly, a² - 2ab + b² factors to (a - b)². While our expression resembles this form, it does not fit perfectly.
-
Trial and error (or AC method): This method involves finding two numbers that add up to 'b' (the coefficient of x) and multiply to 'ac' (the product of the coefficient of x² and the constant term). Let's try this for x² + 4x + 12:
We need two numbers that add up to 4 and multiply to 12 (1 * 12). The pairs of factors of 12 are (1, 12), (2, 6), (3, 4), (-1, -12), (-2, -6), (-3, -4). None of these pairs add up to 4.
The Significance of the Discriminant
The fact that we couldn't find two numbers that satisfy both conditions points to a crucial concept in algebra: the discriminant. The discriminant (Δ) of a quadratic expression ax² + bx + c is given by the formula:
Δ = b² - 4ac
For our expression, x² + 4x + 12, the discriminant is:
Δ = (4)² - 4 * (1) * (12) = 16 - 48 = -32
The discriminant tells us about the nature of the roots (solutions) of the corresponding quadratic equation.
-
Δ > 0: The quadratic equation has two distinct real roots. The quadratic expression can be factored into two distinct linear factors.
-
Δ = 0: The quadratic equation has one repeated real root. The quadratic expression is a perfect square trinomial.
-
Δ < 0: The quadratic equation has no real roots. The quadratic expression cannot be factored using real numbers.
Since the discriminant of x² + 4x + 12 is -32 (a negative value), it means the expression cannot be factored using real numbers.
Factoring with Complex Numbers
While we can't factor x² + 4x + 12 using real numbers, we can factor it using complex numbers. Complex numbers involve the imaginary unit i, where i² = -1. To factor using complex numbers, we can use the quadratic formula:
x = [-b ± √(b² - 4ac)] / 2a
For x² + 4x + 12:
x = [-4 ± √((-32))] / 2 = [-4 ± √(32)i] / 2 = [-4 ± 4√(2)i] / 2 = -2 ± 2√(2)i
Therefore, the roots are x = -2 + 2√(2)i and x = -2 - 2√(2)i. We can express the factored form as:
(x - (-2 + 2√(2)i))(x - (-2 - 2√(2)i)) = (x + 2 - 2√(2)i)(x + 2 + 2√(2)i)
Why This is Important: Implications for Solving Quadratic Equations
The inability to factor x² + 4x + 12 using real numbers directly impacts how we solve the corresponding quadratic equation: x² + 4x + 12 = 0. Since it doesn't factor nicely, we must rely on the quadratic formula to find the roots, which will be complex numbers. This highlights the importance of understanding the discriminant – it tells us whether we can expect real or complex solutions when solving quadratic equations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Forgetting to check for common factors: Always begin by looking for a greatest common factor (GCF) before attempting other factoring methods.
-
Incorrectly applying the difference of squares: Remember, this only works for expressions of the form a² - b².
-
Misinterpreting the discriminant: A negative discriminant does not mean the expression is unfactorable; it simply means it can't be factored using real numbers.
-
Making arithmetic errors: Carefully check your calculations throughout the factoring process.
Expanding Your Understanding: Further Exploration of Quadratic Expressions
Understanding quadratic expressions is crucial for various mathematical concepts. Here are some areas to explore further:
-
Graphing quadratic functions: The graph of a quadratic function (y = ax² + bx + c) is a parabola. The discriminant helps determine the parabola's intersection with the x-axis (the roots).
-
Completing the square: This technique is useful for solving quadratic equations and converting the quadratic expression into vertex form, which reveals the parabola's vertex (its turning point).
-
The relationship between roots and coefficients: Vieta's formulas describe the relationships between the roots of a quadratic equation and its coefficients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can all quadratic expressions be factored? A: All quadratic expressions can be factored using complex numbers. However, not all quadratic expressions can be factored using real numbers.
-
Q: What if I get stuck while factoring? A: Review the steps, double-check your calculations, and consider using the quadratic formula to find the roots, then work backward to the factored form.
-
Q: Why is factoring important? A: Factoring simplifies expressions, helps solve equations, and provides valuable insights into the nature of quadratic functions.
Conclusion
Factoring the quadratic expression x² + 4x + 12 demonstrates the importance of understanding the discriminant and the use of complex numbers in algebra. While it cannot be factored using only real numbers, factoring with complex numbers reveals the complete solution set of the corresponding quadratic equation. Mastering quadratic factoring techniques, including the use of the discriminant and complex numbers, is fundamental for success in higher-level mathematics. Remember to always check your work and understand the underlying concepts, not just the steps. This deeper understanding will make tackling more complex problems significantly easier in the future.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Factorise X 2 4x 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.