3 2/3 As A Decimal
sicesbrasil
Sep 23, 2025 · 6 min read
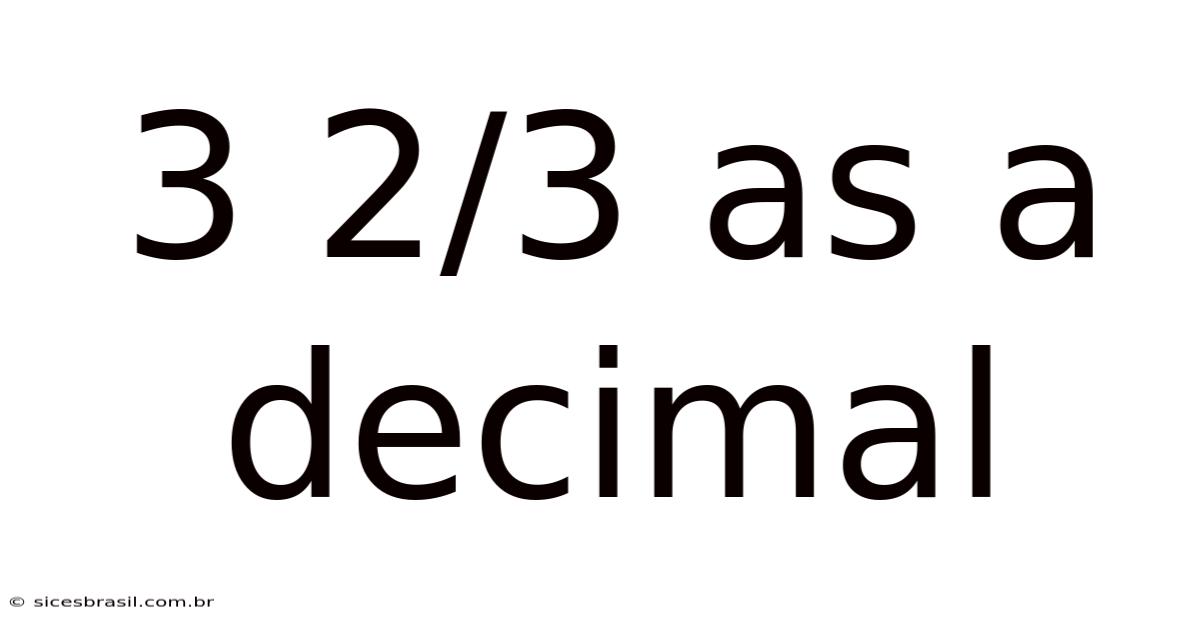
Table of Contents
Understanding 3 2/3 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide
Many mathematical concepts can seem daunting at first, but with a little patience and the right approach, they become surprisingly straightforward. Converting fractions to decimals is one such concept. This article will guide you through the process of converting the mixed number 3 2/3 into its decimal equivalent, providing a detailed explanation suitable for learners of all levels. We’ll explore the underlying principles, various methods, and even address some frequently asked questions, leaving you with a solid understanding of this important mathematical skill.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Fractions
Before we delve into the conversion, let's refresh our understanding of mixed numbers and fractions. A mixed number combines a whole number and a fraction, like 3 2/3. This represents 3 whole units plus two-thirds of another unit. A fraction, on the other hand, expresses a part of a whole. The top number is the numerator, indicating the number of parts we have, and the bottom number is the denominator, indicating the total number of parts the whole is divided into.
Method 1: Converting the Fraction to a Decimal, Then Adding the Whole Number
This is a common and intuitive approach. We'll first convert the fractional part (2/3) into a decimal, and then add the whole number (3).
Step 1: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
To convert the fraction 2/3 to a decimal, we simply divide the numerator (2) by the denominator (3):
2 ÷ 3 = 0.666666...
Notice that the division results in a repeating decimal. The digit 6 repeats infinitely. We often represent this using a bar over the repeating digit(s): 0.6̅
Step 2: Add the Whole Number
Now, add the whole number part (3) to the decimal equivalent of the fraction (0.666666...):
3 + 0.666666... = 3.666666...
Therefore, 3 2/3 as a decimal is approximately 3.666666... or 3.6̅. In practice, we might round this to a certain number of decimal places depending on the context. For example, rounded to two decimal places, it would be 3.67.
Method 2: Converting the Mixed Number to an Improper Fraction, Then to a Decimal
This method involves converting the mixed number into an improper fraction first, before performing the division. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator.
Step 1: Convert to an Improper Fraction
To convert 3 2/3 to an improper fraction, we multiply the whole number (3) by the denominator (3), add the numerator (2), and keep the same denominator (3):
(3 × 3) + 2 = 11
The improper fraction is 11/3.
Step 2: Divide the Numerator by the Denominator
Now, divide the numerator (11) by the denominator (3):
11 ÷ 3 = 3.666666...
This again gives us the same repeating decimal: 3.6̅, approximately 3.67 when rounded to two decimal places.
Understanding Repeating Decimals
The result of converting 3 2/3 to a decimal highlights an important aspect of decimal representation: repeating decimals. Not all fractions convert to terminating decimals (decimals that end). Fractions with denominators that have prime factors other than 2 and 5 will result in repeating decimals. In this case, the denominator 3 is a prime number other than 2 or 5, leading to the repeating decimal 0.6̅.
Rounding Repeating Decimals
Since we can’t write an infinite number of 6s, we often round repeating decimals to a specific number of decimal places. The common methods for rounding are:
-
Rounding to the nearest tenth: We look at the hundredths place. If it's 5 or greater, we round the tenths place up. Otherwise, we keep the tenths place the same. In this case, 3.666... rounded to the nearest tenth is 3.7.
-
Rounding to the nearest hundredth: We look at the thousandths place. If it's 5 or greater, we round the hundredths place up. Otherwise, we keep the hundredths place the same. In this case, 3.666... rounded to the nearest hundredth is 3.67.
-
Truncating: This involves simply cutting off the decimal after a certain number of places. For example, truncating 3.666... to two decimal places gives 3.66.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversion
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill with numerous real-world applications:
-
Calculating Percentages: Many percentage calculations require working with decimals. For example, calculating 2/3 of a quantity involves converting 2/3 to a decimal (0.666...) and then multiplying.
-
Financial Calculations: Interest rates, discounts, and other financial calculations often use decimals.
-
Measurement and Engineering: Precise measurements often involve decimals, and converting fractional measurements to decimals is necessary for various calculations.
-
Scientific Calculations: Many scientific formulas and calculations utilize decimals for precision and ease of computation.
-
Data Analysis: Decimals are widely used in data analysis and statistics for representing proportions and probabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Why does 2/3 result in a repeating decimal?
A1: The fraction 2/3 results in a repeating decimal because the denominator (3) has a prime factor (3) other than 2 or 5. Only fractions with denominators that are only composed of 2s and 5s will have a terminating decimal representation.
Q2: How do I choose the appropriate level of rounding?
A2: The level of rounding depends on the context. For general purposes, rounding to two or three decimal places is often sufficient. However, in scientific calculations or engineering applications, higher precision might be necessary.
Q3: Can all fractions be expressed as decimals?
A3: Yes, all fractions can be expressed as decimals. Some fractions will result in terminating decimals, while others will result in repeating decimals.
Q4: Is there a way to express 3.6̅ without using the bar notation?
A4: While the bar notation (3.6̅) is the most concise and accurate representation, you can sometimes express it as a fraction (11/3) or use a very precise approximation with a large number of decimal places. However, these are not as precise as the bar notation.
Q5: What if the fraction was a different mixed number? How would the process change?
A5: The process remains the same regardless of the mixed number. You would follow the same steps, converting the fractional part to a decimal and then adding the whole number, or converting the mixed number to an improper fraction and then dividing.
Conclusion
Converting the mixed number 3 2/3 to its decimal equivalent, approximately 3.666..., is a straightforward process that involves understanding fractions, division, and potentially repeating decimals. Mastering this skill is essential for various mathematical applications, extending beyond the classroom into many aspects of daily life. Remember to choose an appropriate rounding method based on the context and the required level of precision. By understanding the underlying principles and the various methods outlined here, you'll be well-equipped to handle similar conversions with confidence.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 2/3 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.