3 16 As A Decimal
sicesbrasil
Sep 22, 2025 · 5 min read
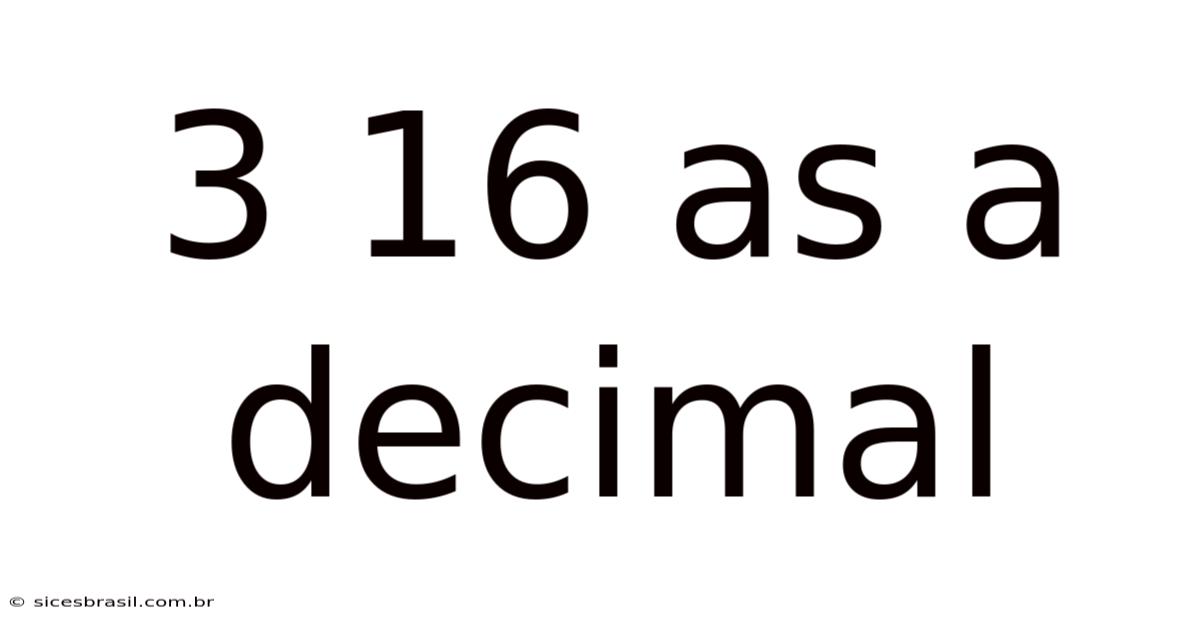
Table of Contents
3/16 as a Decimal: A Comprehensive Guide to Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
Understanding how to convert fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will delve into the conversion of the fraction 3/16 to its decimal equivalent, explaining the process in detail and exploring related concepts. We'll cover multiple methods, address common misconceptions, and provide practical applications to solidify your understanding. This article will serve as a valuable resource for students, educators, and anyone seeking a deeper grasp of decimal representation.
Introduction: Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we dive into converting 3/16 to a decimal, let's briefly review the concepts of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two numbers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). A decimal is a way of representing a number using base-10, where each digit to the right of the decimal point represents a power of ten (tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on).
Converting a fraction to a decimal essentially means finding the equivalent decimal representation of that fraction. This is achieved by dividing the numerator by the denominator.
Method 1: Long Division
The most straightforward method for converting 3/16 to a decimal is through long division. We divide the numerator (3) by the denominator (16):
0.1875
16 | 3.0000
-16
140
-128
120
-112
80
-80
0
Therefore, 3/16 as a decimal is 0.1875. This method is reliable and works for all fractions. It's particularly helpful for understanding the underlying process of fraction-to-decimal conversion.
Method 2: Using Equivalent Fractions
Another approach involves creating an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). While this method isn't always directly applicable (as is the case with 3/16), understanding it provides valuable insight into fractional relationships.
Unfortunately, 16 does not easily convert to a power of 10. We can't find a whole number to multiply both the numerator and denominator by to get a power of 10 as the denominator. This is why long division is the preferred method for this specific fraction.
Method 3: Using a Calculator
Modern calculators make the conversion process extremely simple. Simply enter "3 ÷ 16" and the calculator will directly display the decimal equivalent: 0.1875. While convenient, relying solely on calculators can hinder a deep understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It's crucial to understand the long division method to grasp the fundamental concept.
Understanding the Decimal Representation: Place Value
The decimal 0.1875 can be broken down by place value:
- 0: Ones place (no whole numbers)
- 1: Tenths place (1/10)
- 8: Hundredths place (8/100)
- 7: Thousandths place (7/1000)
- 5: Ten-thousandths place (5/10000)
This emphasizes that the decimal represents a sum of fractional parts: (1/10) + (8/100) + (7/1000) + (5/10000) = 0.1875
Repeating and Terminating Decimals
It's important to distinguish between terminating and repeating decimals. A terminating decimal, like 0.1875, has a finite number of digits after the decimal point. A repeating decimal, on the other hand, has a digit or group of digits that repeat infinitely. For example, 1/3 = 0.3333... (the 3 repeats infinitely).
The fraction 3/16 is an example of a terminating decimal because the division process eventually results in a remainder of 0.
Practical Applications of Decimal Conversion
Converting fractions to decimals is crucial in various real-world scenarios:
- Measurements: When dealing with measurements involving inches, centimeters, or other units, converting fractions to decimals provides greater precision. For example, 3/16 of an inch is 0.1875 inches.
- Financial Calculations: Calculating percentages, interest rates, or profit margins often involves working with fractions and decimals.
- Engineering and Design: In engineering and design, precise measurements and calculations are paramount, requiring a strong understanding of both fractions and decimals.
- Data Analysis and Statistics: When working with data, converting fractions to decimals often facilitates calculations and statistical analysis.
- Computer Programming: Many programming languages use decimal representations for numerical computations.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Incorrect placement of the decimal point: Ensure the decimal point is correctly placed during long division.
- Rounding errors: When rounding decimals, understand the impact on accuracy. For example, rounding 0.1875 to 0.19 introduces a small error.
- Confusing fractions and decimals: While representing the same value, fractions and decimals have different structures and require distinct operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Q: Can all fractions be converted to terminating decimals?
A: No. Only fractions whose denominators can be expressed as a power of 2 or 5 (or a combination of both) will result in terminating decimals. Fractions with other prime factors in their denominators (like 3, 7, 11, etc.) will result in repeating decimals.
-
Q: What if I get a remainder other than zero in long division?
A: If you encounter a non-zero remainder that repeats during long division, it indicates a repeating decimal. You'll need to identify the repeating pattern and represent it using a bar notation (e.g., 0.333... is written as 0.3̅).
-
Q: Is there a quicker way to convert fractions to decimals besides long division?
A: For simple fractions with denominators that are powers of 10, you can directly convert by adjusting the numerator's position relative to the decimal point. However, long division remains a reliable method for all fractions.
-
Q: What are the applications of converting 3/16 to a decimal in real-world situations?
A: This conversion is useful in various applications such as machining (measuring precise dimensions), cooking (measuring ingredients), and various engineering contexts where precision is important.
Conclusion: Mastering Fraction-to-Decimal Conversion
Mastering the conversion of fractions to decimals is an essential mathematical skill. The long division method, although seemingly simple, is the most reliable approach for accurately converting any fraction to its decimal equivalent. While calculators provide convenience, understanding the underlying principles ensures you can confidently tackle fraction-to-decimal conversions and apply this knowledge to various real-world problems. The conversion of 3/16 to 0.1875 provides a concrete example that solidifies this understanding, emphasizing the importance of both accuracy and the ability to interpret the resulting decimal representation. Remember to practice regularly to build confidence and proficiency in this crucial mathematical skill.
Latest Posts
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 3 16 As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.